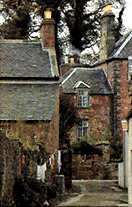Not all Elricks decend from
Scotland. Some came from Germany, Norway and other Locations.
Scotland Pictured here has the village of Elrick. Elrick (Scottish Gaelic:
An Eilreig) is a small village on the
A944 road 7+1⁄2 miles (12 km) west of the city of Aberdeen. The name derives
from a Gaelic word
meaning a place where deer were driven for hunting. Elrick is also a common
surname in the local area.
|
According to 9th and 10th century literature, the Gaelic kingdom
of Dál Riata was founded on the west coast of Scotland in the 6th
century. In the following century Irish missionary Columba would
found a monastery on Iona and introduce the previously pagan Scotti
to Celtic Christianity, and with less success the Picts of Pictland.King Nechtan of Pictland would later choose to expel the Columban
church in favour of the Roman, principally to restrict the influence
of the Scoti on his kingdom and to avoid a war with Northumbria.In the same period Angles had conquered the previously Brythonic
territory south of the Clyde and Forth, initially creating the
Anglo Saxon kingdom of Bernicia, later becoming a part of the
Kingdom
of Northumbria. Towards the end of the 8th century all three
kingdoms
would be raided, settled and to some extent come under Viking
control.
Successive defeats by the Norse would force the Picts and Scoti to
cease
their historic hostility to each other and unite in the 9th Century,
to form the Kingdom of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland was united
under the descendants of Kenneth MacAlpin, first king of a united
Scotland.His descendants, known to modern historians as the House of Alpin,
would fight amongst each other during frequent disputed successions.
The
last Alpin king, Malcolm II, died without issue and the kingdom
passed
through his daughter's son, Duncan I, who started a new line of
kings
known to modern historians as the House of Dunkeld or Canmore. The
last Dunkeld king, Alexander III, died leaving only a single infant
granddaughter as heir. When Margaret, Maid of Norway herself died in
a tragic shipwreck en route to Scotland. England, under Edward I,
would take advantage of the questioned succession in Scotland to
launch
a series of conquests into Scotland. The resulting Wars of Scottish
Independence were fought as Scotland passed back and forth between
the
House of Balliol and the House of Bruce. Scotland's ultimate victory
in
the Wars of Independence under David II would confirm Scotland as a
fully
independent and sovereign kingdom. When David II died without issue,
his
nephew Robert II established the House of Stuart, which would rule
Scotland
uncontested. James VI, Stuart king of Scotland, would also inherit
the throne
of England and the Stuart kings and queens would rule both
independent
kingdoms until the Act of Union in 1707 merged the two kingdoms into
a new
state, the Kingdom of Great Britain. Queen Anne was the last Stuart
monarch,
ruling until 1714. Since 1714, the succession of the British
monarchs of the
houses of Hanover and Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (Windsor) has been due
to their |